Brain disease ATP is a critical subject that touches millions of lives globally, impacting both individuals and families in profound ways. Understanding its complexities can empower patients, caregivers, and healthcare professionals to navigate this challenging terrain more effectively. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve deep into the intricacies of brain diseases, with a specific focus on ATP-related mechanisms, offering actionable insights and evidence-based strategies for managing and overcoming these conditions.
Our brains are the most complex organs in our bodies, and when diseases arise, they can disrupt our cognitive, emotional, and physical well-being. From neurodegenerative disorders to metabolic brain conditions, the role of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) cannot be overstated. This molecule serves as the energy currency of cells, and its dysfunction can lead to severe consequences for brain health. By exploring the relationship between ATP and brain diseases, we aim to provide a clearer understanding of this vital connection.
Whether you are a patient seeking answers, a caregiver looking for guidance, or a healthcare professional searching for the latest research, this guide offers a wealth of information. We will cover everything from the basics of brain diseases and ATP to advanced strategies for prevention, treatment, and management. Let's embark on this journey together to unlock the secrets of mastering the complexities of brain disease ATP.
Read also:Kannada Movierulz Your Ultimate Guide To Exploring The World Of Kannada Cinema
Table of Contents
- Overview of Brain Disease ATP
- The Role of ATP in Brain Function
- Common Brain Diseases Linked to ATP Dysfunction
- Symptoms and Early Warning Signs
- Diagnosis of Brain Diseases Related to ATP
- Treatment Options and Therapies
- Preventive Measures for Brain Disease ATP
- Lifestyle Changes to Support Brain Health
- Current Research and Future Directions
- Resources and Support for Patients and Caregivers
Overview of Brain Disease ATP
Brain disease ATP refers to a range of neurological conditions where ATP production or utilization is compromised. ATP is essential for maintaining cellular functions, including neurotransmission, synaptic plasticity, and neuronal metabolism. When ATP levels decline, neurons become vulnerable to damage and dysfunction, leading to various brain diseases.
In this section, we will explore:
- What ATP is and why it matters for brain health
- How ATP dysfunction contributes to brain diseases
- The importance of early intervention in managing ATP-related brain conditions
What Is ATP?
ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, is often referred to as the "energy currency" of cells. It stores and transfers chemical energy within cells, enabling vital processes such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, and biosynthetic reactions. In the brain, ATP plays a crucial role in maintaining neuronal activity and supporting cognitive functions.
Why ATP Matters for Brain Health
The brain consumes approximately 20% of the body's total energy, despite accounting for only 2% of body weight. This high energy demand makes the brain particularly susceptible to ATP-related disruptions. Conditions such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and traumatic brain injury have all been linked to impaired ATP production or utilization.
The Role of ATP in Brain Function
ATP is indispensable for proper brain function. It powers numerous processes that keep neurons healthy and active. In this section, we will examine the specific roles ATP plays in the brain and how its dysfunction can lead to disease.
Key Functions of ATP in the Brain
- Facilitating neurotransmitter release and reuptake
- Supporting ion channel activity and maintaining membrane potential
- Driving protein synthesis and repair mechanisms
Research shows that ATP depletion can trigger a cascade of events leading to neuronal death. For instance, in ischemic stroke, the sudden loss of blood flow disrupts ATP production, causing neurons to malfunction and die.
Read also:Who Is Esther Krakue Husband Unveiling The Life And Love Story
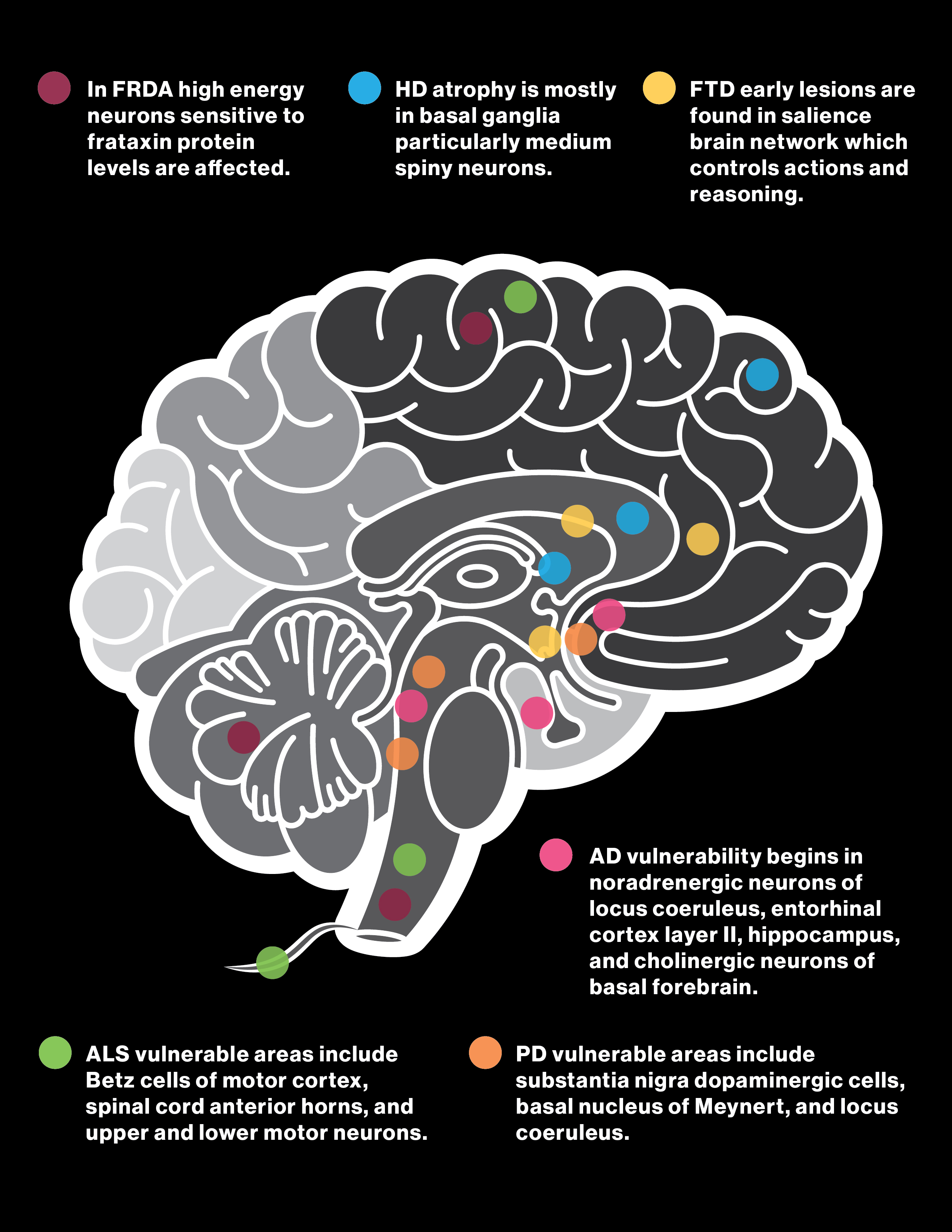
Common Brain Diseases Linked to ATP Dysfunction
Several brain diseases have been directly or indirectly linked to ATP dysfunction. Understanding these conditions can help in developing targeted therapies and interventions. Below are some of the most common brain diseases associated with ATP-related issues:
Alzheimer's Disease
Alzheimer's disease is characterized by the accumulation of amyloid-beta plaques and neurofibrillary tangles, which disrupt ATP production in mitochondria. This energy deficit contributes to neuronal degeneration and cognitive decline.
Parkinson's Disease
Parkinson's disease involves the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra. Studies suggest that mitochondrial dysfunction and impaired ATP synthesis play a significant role in this neurodegenerative process.
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
TBI causes a sudden drop in ATP levels due to disrupted glucose metabolism and oxygen supply. This energy crisis can exacerbate secondary injury and lead to long-term cognitive impairments.
Symptoms and Early Warning Signs
Recognizing the symptoms of brain diseases linked to ATP dysfunction is crucial for early diagnosis and intervention. In this section, we will outline the common signs and symptoms to watch out for:
- Memory loss and cognitive decline
- Mood changes and emotional instability
- Physical symptoms such as tremors, muscle weakness, or balance problems
Early detection can significantly improve outcomes, as timely interventions can slow disease progression and enhance quality of life.
Diagnosis of Brain Diseases Related to ATP
Diagnosing brain diseases with ATP involvement requires a combination of clinical assessments, imaging studies, and laboratory tests. This section will discuss the diagnostic tools and techniques used by healthcare professionals:
Clinical Evaluation
Healthcare providers begin with a thorough medical history and physical examination. They assess cognitive function, motor skills, and other neurological domains to identify potential ATP-related issues.
Imaging Techniques
MRI and PET scans are commonly used to visualize brain structures and metabolic activity. These imaging modalities can detect abnormalities in ATP production and utilization.
Laboratory Tests
Blood tests and cerebrospinal fluid analysis can provide insights into mitochondrial function and ATP levels. Genetic testing may also be employed to identify inherited predispositions to ATP-related brain diseases.
Treatment Options and Therapies
Treating brain diseases associated with ATP dysfunction involves a multidisciplinary approach. In this section, we will explore the various treatment options available:
Pharmacological Interventions
Medications targeting mitochondrial function and ATP production are being developed. Examples include coenzyme Q10, creatine, and nicotinamide riboside, which aim to enhance energy metabolism in the brain.
Non-Pharmacological Therapies
Therapies such as cognitive rehabilitation, physical exercise, and dietary modifications can support brain health and improve ATP-related symptoms.
Preventive Measures for Brain Disease ATP
Prevention is key to managing ATP-related brain diseases. In this section, we will discuss strategies to reduce the risk of developing these conditions:
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Adopting a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, engaging in regular physical activity, and ensuring adequate sleep can promote brain health and ATP production.
Regular Medical Checkups
Early detection through routine screenings can help identify potential issues before they escalate into full-blown diseases.
Lifestyle Changes to Support Brain Health
Making lifestyle adjustments can have a profound impact on brain health and ATP function. This section highlights specific changes individuals can make:
- Incorporating brain-boosting foods like fatty fish, nuts, and berries into your diet
- Practicing mindfulness and stress reduction techniques
- Avoiding harmful substances such as tobacco and excessive alcohol
Current Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research in the field of ATP and brain diseases offers hope for new treatments and therapies. This section will highlight some of the latest advancements:
Emerging Technologies
Advances in gene therapy and stem cell research hold promise for restoring ATP function in damaged neurons.
Clinical Trials
Several clinical trials are currently investigating the efficacy of novel drugs targeting ATP pathways in brain diseases.
Resources and Support for Patients and Caregivers
For those affected by ATP-related brain diseases, accessing reliable resources and support networks is essential. This section provides a list of helpful organizations and tools:
- Alzheimer's Association
- Parkinson's Foundation
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)
Conclusion
Mastering the complexities of brain disease ATP requires a comprehensive understanding of its mechanisms, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. By staying informed and proactive, individuals can take charge of their brain health and reduce the risk of ATP-related conditions. We encourage readers to share this guide, leave comments, and explore additional resources to deepen their knowledge. Together, we can make strides toward a healthier future for all.